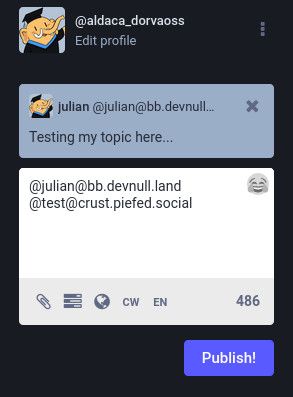
NodeBB <> Lemmy federation issue (re: nullable image/icon)
-
nutomic@lemmy.ml reported a federation issue with a NodeBB instance and we debugged it. It turns out Lemmy is unable to handle actors who have
imageoriconset tonull.Lemmy is taking steps to handle this (source, source), and NodeBB will update its actor logic to omit properties without an avatar or cover photo set.
-
 undefined nodebb@fosstodon.org shared this topic on
undefined nodebb@fosstodon.org shared this topic on
-
-
evan@cosocial.ca I had no idea that was the case. That is very good to know and having it called out in some sort of best practices doc (an existing w3c explainer?) would be helpful :smile:
-
NodeBB v4.6.1 contains the fix so that if an avatar and cover photo are not set, they are not included in the ActivityPub actor data.
-
@julian @evan aside from potentially causing null pointer exceptions when you try to dereference null, using null is equivalent to just leaving out the statement in the first place. there's no reason to use null. the only time you'd need null values is if your schema required a certain key to be present but allowed the value to be nullable, which is generally a bad idea compared to just making the key optional. tony hoare, the inventor of null, called it their "billion-dollar mistake".
-
@julian @evan aside from potentially causing null pointer exceptions when you try to dereference null, using null is equivalent to just leaving out the statement in the first place. there's no reason to use null. the only time you'd need null values is if your schema required a certain key to be present but allowed the value to be nullable, which is generally a bad idea compared to just making the key optional. tony hoare, the inventor of null, called it their "billion-dollar mistake".
trwnh@mastodon.social said in NodeBB <> Lemmy federation issue (re: nullable image/icon):
> using null is equivalent to just leaving out the statement in the first place.That's not true, there are specific scenarios where having an explicit "no value" is significant vs "missing value"...
-
@julian if you give me any specific examples of when you would want to use null, i can recommend better alternatives. generally, it's always possible that there is missing information.
-
@julian love to see the reports of cross project colab!
-
@julian if you give me any specific examples of when you would want to use null, i can recommend better alternatives. generally, it's always possible that there is missing information.
trwnh@mastodon.social found one.
NodeBB uses
audienceto denote which audience an object (or context) belongs to.Posts and Topics in NodeBB can belong to no context at all.
nullwould be the way to communicate this, since omission might mean one isn't specified.Likewise, a Move(Context) where a topic is moved out of a category but not into another. You probably shouldnt omit
targetthere. -
@julian no, null is the same as nothing. what you want is more like [] (the empty set). in the case where you Move something without a target, you should be sending an Update instead.
-
@julian no, null is the same as nothing. what you want is more like [] (the empty set). in the case where you Move something without a target, you should be sending an Update instead.
@julian but more generally my question is, what practical application would you need to make use of an empty set []? like, a consumer encountering a value should do A, encountering a null or missing property should do B, encountering an empty set should do C... what is the difference between B and C?
-
@julian but more generally my question is, what practical application would you need to make use of an empty set []? like, a consumer encountering a value should do A, encountering a null or missing property should do B, encountering an empty set should do C... what is the difference between B and C?
trwnh@mastodon.social receiving a Move(Context) where target is null would tell NodeBB to move the topic to -1, uncategorized.
For those not supporting the catch-all bucket, deleting the context is ok too.
-
@julian so this is still in effect a Remove or Update, not a Move. if you wanted it to be a Move, you would instead have an "uncategorized" category whose id is /categories/-1 or something like that.
-
@julian if you give me any specific examples of when you would want to use null, i can recommend better alternatives. generally, it's always possible that there is missing information.
trwnh@mastodon.social oh, another one.
Glitch-soc apparently lets you hide follower counts, and federates a -1. That works but
nullwould be a more explicit statement that the follower collection is hidden/not accessible. -
@julian leaving out the totalItems statement entirely would do the same thing. the problem is when you ignore the (lack of) information presented and synthesize your own.
you could also define a vocab term for "hidden" or "unavailable", although this isn't much better than leaving it out in the first place
-
@julian leaving out the totalItems statement entirely would do the same thing. the problem is when you ignore the (lack of) information presented and synthesize your own.
you could also define a vocab term for "hidden" or "unavailable", although this isn't much better than leaving it out in the first place
trwnh@mastodon.social leaving out totalitems is absolutely not the same as explicitly declaring a null value. You don't know whether the implementation just didn't send totalItems or whether it was omitted on purpose.
-
@julian what's the difference between "not sending" vs "omitting"? those are synonyms
-
@julian what's the difference between "not sending" vs "omitting"? those are synonyms
trwnh@mastodon.social not sent due to implementation differences, rather.
-
trwnh@mastodon.social not sent due to implementation differences, rather.
@julian there's no difference on the consuming side (and in many programming languages you can check for truthiness with something like `if x.get("totalItems")` which defaults to returning null if missing anyway)
functionally, you either have the information, or you don't